Learning to operate an EHR system is complex. They manage patient history, clinician activity, and billing cycle. They use massive quantities of patient data to improve care using historical patterns that signify a likely diagnosis. They coordinate care and sound warnings of probable adverse events.
With that complexity, mastery of the software does not come easily. Yet they are so core to hospital operations that clinicians have little choice but to master their user interface and workflow procedures.
Trying to master an EHR in the traditional classroom setting appears to slow down clinicians and reduce productivity and billable hours. On the other hand, reducing EHR training time through online eLearning holds great potential for cutting costs.
Furthermore, if online training could lead to increased productivity as well, additional financial and performance benefits would accrue.
Study Design
426 inpatient and outpatient providers received an Amplifire course in three modules covering the topic of operating the EHR system.
Module 1: Clinical Review
Module 2: Orders and In Basket
Module 3: Notes, Letters, and Documentation
UCHealth wanted to eliminate classroom training and adopt virtual training methods. They chose the online Amplifire platform for EHR training for one year (and continue to do so). UCHealth then analyzed time saved for providers trained online and compared their EHR proficiency with providers who learned in the classroom.
Research indicates that user ratings on the quality of training are the single greatest predictor of overall Electronic Health Record (EHR) user experience.1 These findings are leading health systems to re-invest in innovative training approaches.
Amplifire developed the EHR training Library in conjunction with UCHealth to help physicians, nurses, and technicians effectively navigate the patient record workflow, reduce onboarding and training time, and optimize use of the EHR system.
EHR Training
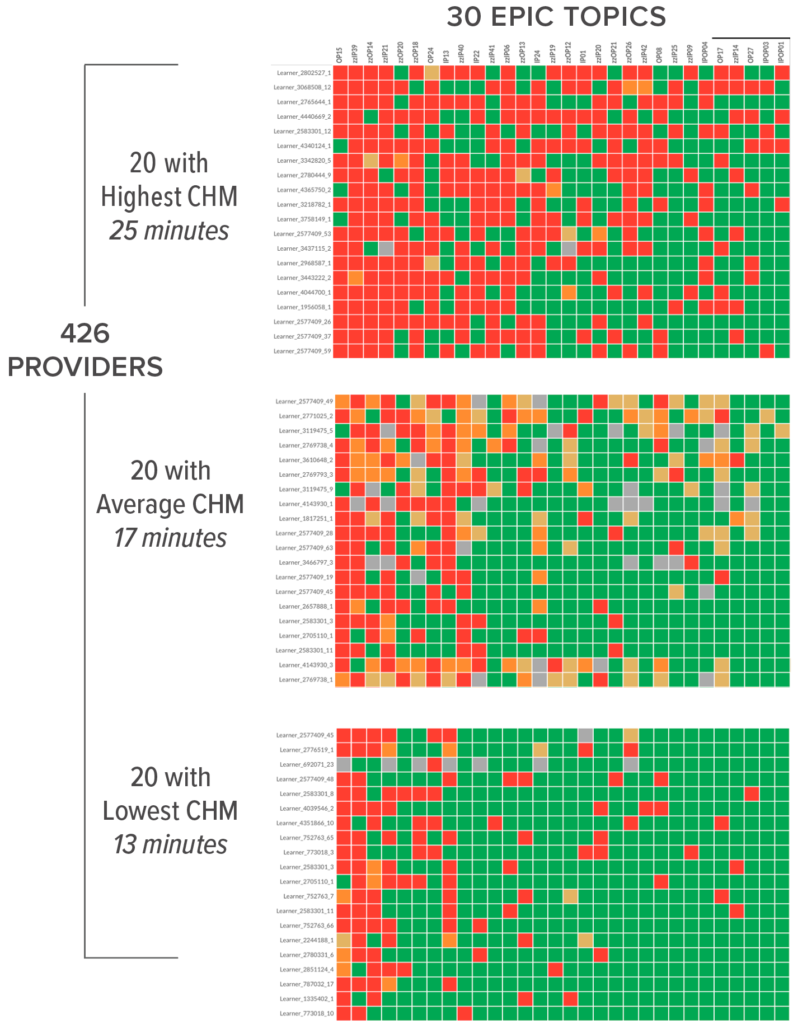
This heatmap comes from Amplifire’s reporting suite and shows providers sorted by their amounts of confidently held misinformation (CHM).
- 426 providers generated 34,076 data points
- 7,837 instances of confidently held misinformation were corrected
- 9,712 instances of uncertainty were corrected
- 16,527 instances of proficiency
- The most initially misinformed providers spent an average of 33 minutes in the platform, while those who were proficient spent only 11 minutes.
- By the end of the course, 100% of the providers were proficient (both confident and correct) on all the material.
To Edit
- 654 clinicians generated 13,080 data points
- 3,008 instances of confidently held misinformation were corrected
- 1,962 instances of uncertainty were corrected

Clinical Implications
Download the full case study to see all of the findings and clinical implications.



